
AI Chat Best Practices — Build Assistants Users Actually Trust (and Enjoy Using)
The Problem with Most AI chat Implementations
You've seen it before: a chat widget demands your email before answering, can't be moved/resized, or traps you in a frustrating loop.
Users notice. They leave, silently, so you have no clue, unless they choose to post a negative review.
The good news? Getting AI chat right is not complicated. It just requires respecting user expectations.
This guide covers 17 essential best practices that separate helpful AI assistants from the kind users actively avoid.
1. Don't Force Identification Before Helping
Bad experience: Chat widget opens. "Please enter your email to continue."
Why it fails: Users want answers, not gatekeeping. Forcing identification before providing any value feels like a data grab, not customer service.
Better approach:
- Answer questions immediately, no data collection required.
- For account-specific queries ("What's my balance?"), then authenticate.
- Make authentication contextual: "To show your account details, I need to verify your identity."
Example flow:
User: "What are your hours?"
Assistant: "We're open Monday through Friday, 9 AM to 6 PM EST."
User: "What's my order status?"
Assistant: "I can check that for you. Please share your email or order number so I can pull up your order."
Help first. Collecting user info should not be your priority at this stage. Authenticate when necessary.
2. Let Users Download Their Chat History
Users should own their conversation data. Period.
Why it matters:
- Legal compliance (GDPR, CCPA).
- User trust and transparency.
- Practical value: users can reference instructions, order numbers, or support details later.
Implementation:
- Add a "Download Chat" or "Email Transcript" option in the chat interface.
- Provide plain text or PDF format.
- Include timestamp, full conversation, and any references (order IDs, ticket numbers).
A well-implemented download feature allows users to export their transcript with a single click. This is basic respect for user data ownership.
3. Allow Users to Reset or Delete Their Chat
Sometimes users want a fresh start. Maybe they shared something by mistake. Maybe they just want a clean slate.
What to provide:
- Reset chat: Clear the conversation from the UI and start fresh (without deleting server logs for your compliance needs).
- Delete personal data: For privacy-conscious users, offer the option to request deletion of their data per GDPR/CCPA requirements.
UI placement:
- Add a "Reset Chat" button in the chat header or menu.
- Include a "Privacy & Data" link in the footer with information about data deletion requests.
Control builds trust. Users should never feel trapped in a conversation.
4. Maintain Context Across Pages (and Channels)
Nothing frustrates users more than repeating themselves.
Within your website:
- If a user starts a conversation on your homepage and navigates to the pricing page, the chat should remember the conversation.
- Use session persistence (cookies, local storage, or session tokens) to maintain chat state across page loads.
Across channels (omnichannel):
- If a user starts on web chat and later texts your WhatsApp number, the assistant should recognize them (with proper authentication).
- This requires unified customer profiles and conversation history across channels.
Example:
User on web chat: "I want to schedule a service appointment."
Assistant: "Sure, what date works for you?"
(User navigates to the services page)
User on same web chat: "How about next Tuesday?"
Assistant: "Tuesday works. What time?"
Seamless context makes your assistant feel intelligent, not robotic.
5. Display Clear Privacy and Terms Policies
Users want to know what happens to their data. Tell them.
What to include in your chat interface:
- A visible link to your privacy policy (in the chat footer or welcome message).
- Clear disclosure if conversations are recorded or monitored.
- Information about data retention ("Chats are stored for 30 days").
- How to request data deletion.
Example welcome message:
"Hi! I'm here to help. By using this chat, you agree to our Privacy Policy and Terms of Service. Your conversations are encrypted and stored securely."
Transparency is not optional. It is table stakes for user trust.
6. Build a Friendly, Flexible UI
Your chat interface should feel helpful, not intrusive.
Essential UI features:
Movable and resizable:
- Users should be able to drag the chat window to a comfortable position.
- On desktop, allow resizing (larger for reading long responses, smaller when multitasking).
- On mobile, support touch gestures (swipe to minimize, drag to reposition).
Streaming responses:
- Show AI responses as they are generated (like ChatGPT), not all at once after a delay.
- This creates a sense of real-time interaction and reduces perceived wait time.
Real-time feedback:
- Typing indicators ("Assistant is typing...").
- Read receipts or acknowledgment when user messages are received.
- Thumbs up/down or star ratings after responses for quality feedback.
Visual polish:
- Clean, modern design with good contrast and readability.
- Support for light and dark modes.
- Smooth animations (fade in/out, not jarring pops).
Modern chat widgets that support these UI features see significantly higher user engagement. These details matter.
7. Support Authenticated User Context
When a user is already logged into your site, the AI assistant should have access to relevant user-specific information.
Why it matters:
- Eliminates redundant authentication within the chat.
- Enables personalized responses based on account data.
- Provides contextual help specific to the user's situation.
Technical approach:
- Host page sets
window.user_contextwith relevant user data as a text blob. - Chat widget passes this context to the backend with each user prompt.
- Context can be refreshed dynamically by the host page as needed.
- Only include data relevant to customer service (account status, preferences, history).
- Never include sensitive credentials (passwords, payment card details).
Example context blob:
window.user_context = "User: Sarah Johnson, Account ID: 78453, Status: Premium member since 2022, Recent order #12345 shipped 2024-01-15, Current balance: $0, Preferred contact: email"
Result:
User: "Where's my order?"
Assistant: "Your order #12345 shipped yesterday and should arrive by Thursday. Would you like the tracking link?"
This pattern works for any authenticated session where user-specific context enhances the conversation.
8. Provide Chat Starters
Not everyone knows what to ask. Help them get started.
What are chat starters?
- Pre-written prompts or buttons that suggest common questions.
- Displayed when the chat first opens or when the conversation is idle.
Examples:
- "Check my order status"
- "Schedule an appointment"
- "See pricing options"
- "Talk to a live agent"
Benefits:
- Reduces friction (users do not have to think about what to type).
- Guides users toward your assistant's strongest capabilities.
- Increases engagement (users are more likely to interact with one-click prompts).
Best practices:
- Limit to 3-4 starters (too many choices create decision paralysis).
- Make them action-oriented and specific.
- Update them based on user context (different starters for logged-in vs. anonymous users).
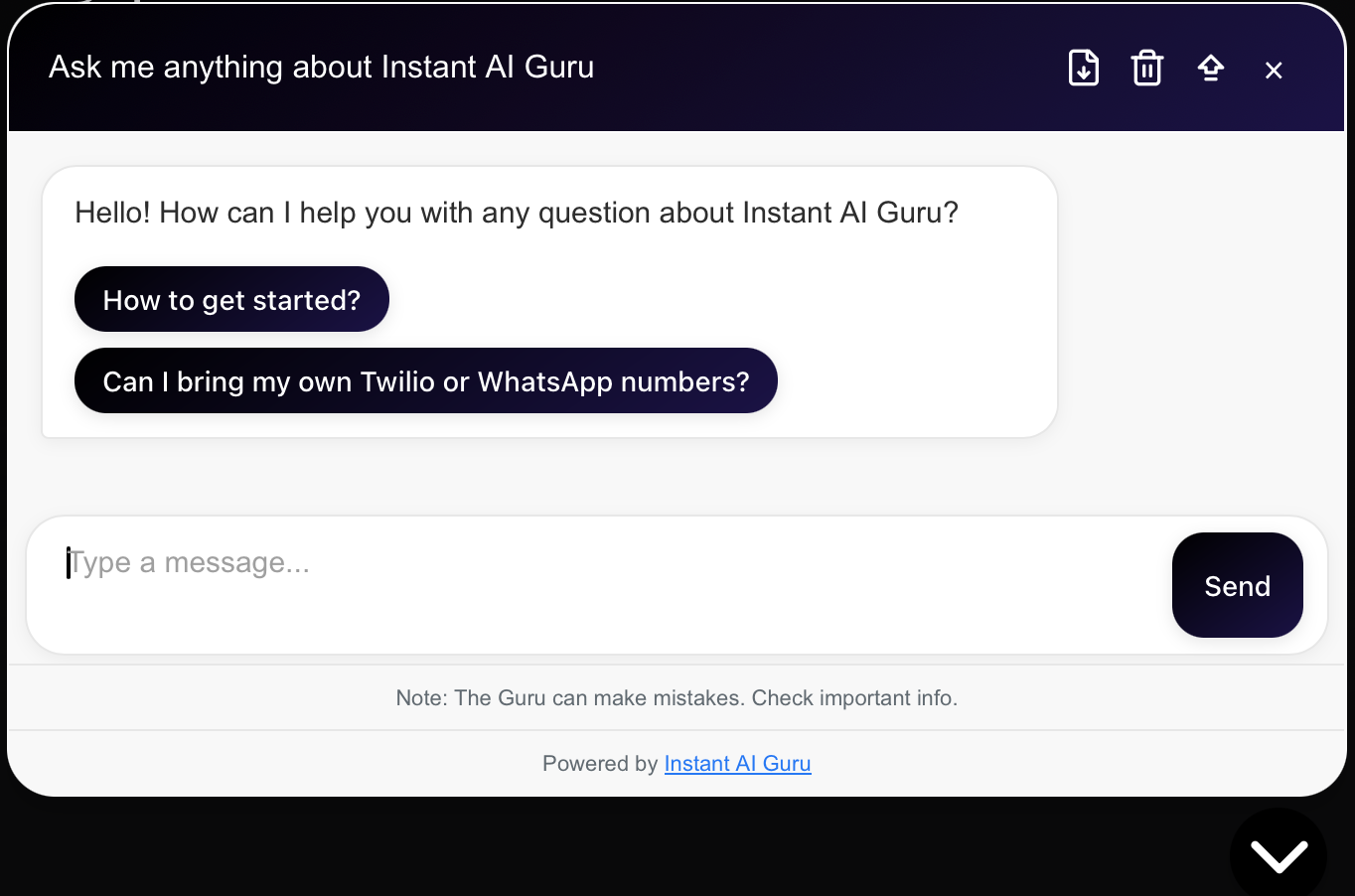
Chat starters in action: one click gets users instant help.
9. Provide Clear Escalation to Human Agents (when available)
Your AI assistant should know its limits and offer a clear path to human help, when available - not every organization can support human escalation, and when they do it may be limited to certain hours or topics.
Why it matters:
- Some questions are too complex, sensitive, or unusual for AI.
- Users trust systems that admit limitations more than those that fake competence.
- A smooth handoff preserves the customer relationship.
How to implement:
- Availability: "Talk to a live agent" should be an option when human support is available (business hours, specific topics).
- Context handoff: When transferring, pass conversation history to the agent so the user does not repeat themselves.
- Clear expectations: "I'm connecting you to Sarah. Average wait time is 2 minutes."
- Fallback triggers: Automatically offer escalation after 2-3 failed attempts to help.
Example:
User: "I need to dispute a charge from three months ago."
Assistant: "I can see your account history, but disputes require human review. Would you like me to connect you to our billing team? I'll share your account details and this conversation with them to save you time."
The best AI assistants know when to step aside.
10. Be Transparent That It's an AI
Do not pretend your AI is human. Users notice. And they do not like being deceived.
Why transparency matters:
- Legal compliance (some jurisdictions require AI disclosure).
- Trust: users adjust their communication style when they know it's AI.
- Manages expectations: users understand why certain requests need human escalation.
How to disclose:
- Opening message: "Hi! I'm your AI assistant. I can help with orders, scheduling, and account questions."
- Widget branding: "Powered by AI" or similar indicator.
- Natural admission: "As an AI assistant, I can't process refunds directly, but I can connect you to someone who can."
What NOT to do:
- Fake typing delays to seem human.
- Use human names without clarifying it's AI.
- Hide behind vague language when you mean to say 'AI'.
Be upfront. Users respect honesty.
11. Handle Errors Gracefully
Things go wrong. Your chat should handle failures without making users feel stuck.
Common failure scenarios:
- Backend API timeout or error.
- AI model fails to generate a response.
- User's internet connection drops.
- Rate limiting or abuse detection triggers.
Best practices for error handling:
- Clear messaging: "I'm having trouble connecting. Please try again in a moment."
- Retry mechanism: Automatic retry with exponential backoff, or a "Try Again" button.
- Fallback options: "While I work on this, you can also email [email protected]."
- Never blame the user: Avoid "You entered an invalid request." Instead: "I couldn't process that. Could you rephrase?"
Connection loss handling:
- Save conversation state locally (localStorage) so users don't lose their place.
- Show a clear "Reconnecting..." indicator.
- Auto-resume when connection is restored.
Errors are inevitable. Graceful recovery is what separates good implementations from bad ones.
12. Optimize for Mobile First
Over 60% of web traffic is mobile. Your chat must work perfectly on small screens.
Mobile-specific considerations:
- Full-screen on mobile: Chat should expand to use available screen space, not be a tiny widget.
- Touch-friendly targets: Buttons and links at least 44×44 pixels (Apple's touch target guideline).
- Readable text: Minimum 16px font size, good contrast.
- Keyboard handling: Input field should push content up when keyboard appears (not obscure the conversation).
- Swipe gestures: Swipe down to minimize, swipe up to expand.
- Fast loading: Lazy load images and components. Users on mobile data hate waiting.
Test on real devices:
- iPhone SE (small screen).
- Android mid-range phones (various screen sizes).
- Tablets in both portrait and landscape.
If your chat works beautifully on desktop but feels clunky on mobile, you are losing most of your audience.
13. Avoid Annoying Proactive Popups
Nothing screams "desperate" like a chat popup appearing 2 seconds after page load.
The problem with instant popups:
- Users have not even read your content yet.
- It interrupts their flow and feels pushy.
- Many users immediately close it and never come back.
Smarter proactive chat strategies:
- Time delay: Wait at least 15-30 seconds before showing any prompt.
- Scroll-based: Show chat after user scrolls 50% down the page (indicates engagement).
- Exit intent: Detect when user is about to leave and offer help then.
- Contextual triggers: On pricing page for 20+ seconds? Offer "Questions about pricing?"
- Returning visitors: If user visited multiple times without chatting, offer help.
Visual approach:
- Start with a small, non-intrusive icon in the corner.
- If appropriate based on triggers above, show a small message bubble: "Need help?" (not a full modal takeover).
- Let users click to expand, don't force it.
Respect the user's browsing experience. Make chat available, not unavoidable.
14. Support Accessibility Standards
Millions of users rely on assistive technologies. Your chat should work for them too.
Key accessibility requirements (WCAG 2.1 Level AA):
- Keyboard navigation: Full chat functionality accessible via keyboard only (Tab, Enter, Escape).
- Screen reader support: Proper ARIA labels, roles, and live regions for new messages.
- Focus management: Clear focus indicators, logical tab order.
- Color contrast: Minimum 4.5:1 ratio for text, 3:1 for UI components.
- Text resizing: Interface remains functional at 200% zoom.
- Alternative text: Images and icons have descriptive alt text.
Testing accessibility:
- Use a screen reader (NVDA on Windows, VoiceOver on Mac/iOS).
- Navigate using only keyboard (no mouse).
- Run automated tools like axe DevTools or WAVE.
Accessible design is not a nice-to-have. It is a legal requirement in many jurisdictions and basic human decency.
15. Show Backend Process Visibility
Users appreciate knowing what the AI is doing, especially during longer responses.
Why it matters:
- Reduces perceived wait time (users see activity, not just a blank screen).
- Builds trust by showing the AI's "thought process."
- Manages expectations for complex queries that take time.
What to show:
- "Analyzing your question..."
- "Searching knowledge base..."
- "Generating response..."
Implementation:
- Display process status as inline messages or subtle status indicators.
- Update in real-time as the backend moves through processing stages.
- Keep messages brief and non-technical.
- Show progress for multi-step operations.
Example flow:
User: "What's the status of all my recent orders?"
[Status: Searching order history...]
[Status: Found 3 orders, retrieving details...]
Assistant: "I found 3 recent orders. Order #12345 shipped yesterday..."
Transparency about backend activity makes the AI feel responsive and trustworthy, not like a black box.
16. Allow Interruption with Context Preservation
Users should be able to interrupt and correct themselves mid-conversation without losing context.
Why it matters:
- Natural conversations include corrections ("Actually, I meant...").
- Prevents frustration from having to wait for wrong responses.
- Saves time for both user and system.
How it works:
- Allow users to send new messages while AI is still generating a response.
- Stop current generation and process the interruption.
- Maintain conversation context, incorporating the correction.
- Acknowledge the correction naturally.
Example:
User: "I need a 60 inch TV"
[AI starts generating response about 60" TVs...]
User: "Actually, make that 75 inch"
[AI stops mid-response]
Assistant: "Got it, looking at 75 inch TVs instead. Here are our top options..."
Technical considerations:
- Implement message queue that prioritizes new user input.
- Cancel ongoing AI generation when new input arrives.
- Pass both the original query and correction to the AI for full context.
This matches how humans naturally interrupt and correct in conversation.
17. Format Code with Copy Support
When your AI assistant shares code snippets, make them easy to read and copy.
Why it matters:
- Users frequently ask for code examples, API calls, or configuration snippets.
- Poorly formatted code is difficult to read and error-prone to manually copy.
- One-click copy prevents transcription errors.
Essential features:
- Monospace font: Use proper code font (Consolas, Monaco, Courier New).
- Copy button: One-click copy to clipboard for each code block.
- Language label: Show the language (Python, JavaScript, SQL, etc.).
- Line numbers: Optional but helpful for longer snippets.
Example display:
User: "How do I make an API call to your service?"
Assistant: "Here's a cURL example:"
Copy curl -X POST https://api.example.com/v1/query \
-H "Content-Type: application/json" \
-d '{"question": "Hello"}'
Supported languages should include:
- Common programming languages (Python, JavaScript, Java, C#, etc.)
- Query languages (SQL, GraphQL)
- Markup languages (HTML, XML, JSON, YAML)
- Shell/terminal commands (bash, PowerShell)
Good code formatting shows attention to developer experience.
Why These Practices Matter
Every one of these best practices serves a single goal: respect the user.
Respect their time (no forced identification, chat starters, smart proactive help).
Respect their data (download transcripts, clear privacy policies, data deletion).
Respect their preferences (movable UI, reset options, mobile optimization).
Respect their context (authenticated sessions, cross-page persistence, human escalation).
Respect their trust (honest AI disclosure, graceful error handling, accessibility support).
When you get these details right, users trust your AI assistant. They engage more. They leave better reviews. They become repeat customers.
When you skip them, your chat becomes another annoying popup that users immediately close.
Implementation Checklist
Use this checklist when deploying or auditing your AI chat:
- ✓ Users can ask questions without logging in or providing contact info upfront.
- ✓ Authentication is contextual and only requested when necessary.
- ✓ Download chat transcript option is visible and functional.
- ✓ Reset chat button is available.
- ✓ Privacy policy and data deletion instructions are linked in the chat interface.
- ✓ Chat context persists across page navigation.
- ✓ Omnichannel context is maintained for identified users.
- ✓ Chat widget is draggable and resizable (desktop) and supports touch gestures (mobile).
- ✓ Responses stream in real-time, not all at once.
- ✓ Typing indicators and feedback mechanisms (thumbs up/down) are present.
- ✓ Authenticated user context is passed securely to the AI backend when users are logged in.
- ✓ Chat starters are displayed and relevant to user context.
- ✓ "Talk to a live agent" option is always available, with smooth handoff and context sharing.
- ✓ Opening message clearly discloses it's an AI assistant.
- ✓ Error messages are clear and helpful with retry options and fallback contact methods.
- ✓ Connection loss is handled gracefully with auto-reconnect.
- ✓ Mobile interface is full-screen, touch-optimized, and fast-loading.
- ✓ Proactive prompts are contextual and delayed, not instant popups.
- ✓ Full keyboard navigation and screen reader support (WCAG 2.1 Level AA).
- ✓ Backend process visibility shows what the AI is doing (searching, analyzing, etc.).
- ✓ Users can interrupt and correct mid-response without losing context.
- ✓ Code snippets styling and one-click copy buttons.
Implementation Reference
For reference, here's how these practices can be implemented in production:
- No gatekeeping: Serve general queries without authentication, request login only for account-specific data.
- Full user control: Provide transcript download, chat reset, and data deletion request options.
- Omnichannel context: Maintain conversation continuity across web, SMS, WhatsApp, and voice channels.
- Transparent privacy: Link to privacy policy, disclose data retention, support GDPR/CCPA requests.
- Polished UI: Implement draggable/resizable widget, streaming responses, and feedback mechanisms.
- Authenticated context: Use
window.user_contextpattern for passing session data to AI backend. - Smart chat starters: Display 3-4 contextual prompts based on page content and user status.
- Human escalation: Provide always-available agent option with context handoff.
- Honest AI disclosure: State in opening message that user is interacting with AI.
- Graceful error handling: Show clear error messages, retry mechanisms, and fallback contact methods.
- Mobile-optimized: Full-screen interface on mobile with 44px touch targets and keyboard-aware layout.
- Smart proactive help: Delay prompts 15-30 seconds, trigger on scroll depth or exit intent.
- Accessibility built-in: ARIA labels, keyboard navigation, 4.5:1 contrast ratios (WCAG 2.1 AA).
- Process visibility: Show real-time status updates during backend operations.
- Interruptibility: Cancel ongoing generation when user sends new input.
- Code formatting: Styleed code blocks and copy buttons.
These practices are becoming standard expectations for production AI chat systems.
Start Building Better AI chat Today
Users expect more than a bot. They expect an assistant that respects their time, protects their data, and actually helps them.
Implement these 17 best practices, and your AI assistant becomes a competitive advantage, not a checkbox feature.
These practices represent the current state of what users expect from AI chat interfaces. Platforms that implement them tend to see higher engagement, better reviews, and more satisfied customers.
As always, your feedback is highly appreciated.
Want to learn more? Read more blogs - Or visit our main page Back to Home